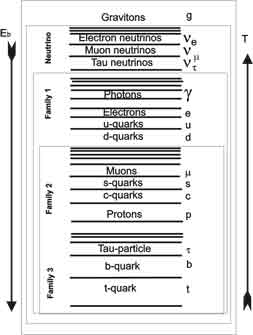
The structure of the fundamental particles and metastable
| The first family of fundamental particles |
|
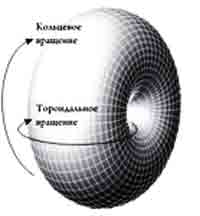
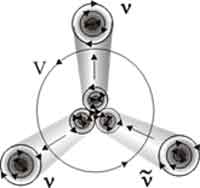
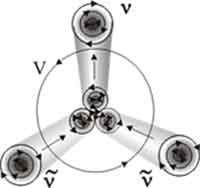
| Electron neutrino - is left vortex ring gravitons. Electron antineutrino is right ring |
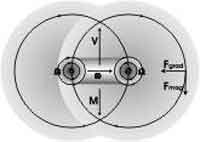 |
| Constant forward motion of neutrinos due to toroidal rotation |
|
|
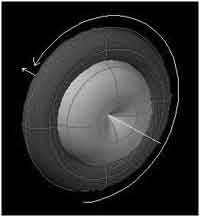 |
Photon is composed of two coaxial neutrinos or antineutrinos two coaxial |
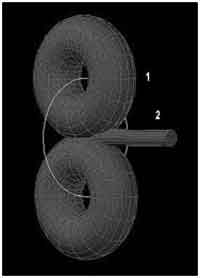 |
| Electron is composed of two electron neutrinos, rotating around a common axis. Positron is composed of two antineutrinos, rotating around a common axis |
|
|
 |
| D-quark scheme: it is formed by addition of the electron antineutrino |
 |
| U-quark scheme: it is formed by addition of neutrinos to the positron |
 |
Formed after inflation foremothers were many vortices in a superdense state. They represented the rays of fluid with its "boiling point." Cool to the boiling point, the gravitons formed larger vortex structures in the form of electron neutrinos and antineutrinos. This is a stable neutral leptons with half-integer spin, participating only in weak and gravitational interactions. Only electron neutrinos and antineutrinos are the elementary particles of matter. All other particles are composite. Further cooling of the medium allowed neutrino interconnected, moving to lower levels. Consolidation into a pair of electron neutrinos and antineutrinos formed photons, electrons and positrons, and two-body interactions with quarks to form protons muon antineutrinos. |
All levels of matter built of neutrinos and antineutrinos. In gravitons (dark matter) has moved only a small fraction of dark energy. In neutrino (substance) moved only a small fraction of dark matter.
|
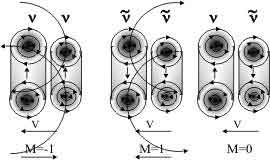
Photon "picked" from two neutrinos (levovintovye photons) or two antineutrinos (pravovintovye photons or "antifotony"). They are aligned with each other and are attracted to the vortex interaction. Neutrinos are constantly changing places, changing their size, and passing through each other on a "game of vortex rings." In light beam contains as much antimatter as matter and |
Why neutrons are unstable stable nucleus of an atom? In the diagram, the structure of the alpha particle is shown that electrons and neutrons are held chain antineutrinos four protons linked by strong vortex interaction.
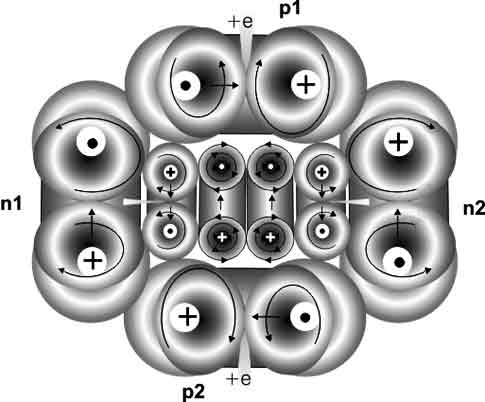
If accelerate particles to high speeds, then the collisions with other particles, or they "stick together", being kept together by pressure on each other, or fly into fragments, of which the formation of new particles. "Sticking" particles can be quite sub-optimal - such lump is fixed as "resonance", then quickly falls apart. But part of the "sticking together" of the particles can be relatively long. They live as long as their internal high kinetic energy, creating inertia. In a "cooling off" due to dissipation of energy composite particles disintegrate. The particle energy is carried away by photons.
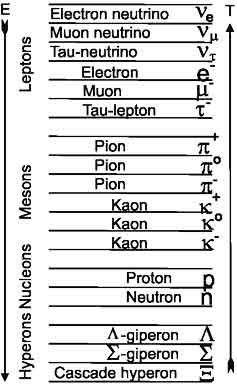 |
The representations of the vortex model can recreate the structure of metastable particles: pions, kaons and hyperons as the excited states of stable particles at higher levels. And where is the antimatter where to look antigalaktiki? Antimatter found in ordinary matter and find him anywhere do not. Proton has eight neutrinos and antineutrinos ten. Therefore, it is more "anti". In the hydrogen atom - the most common element - contains the same number of neutrinos (10) and an antineutrino (10) |
| The second family of fundamental particles |
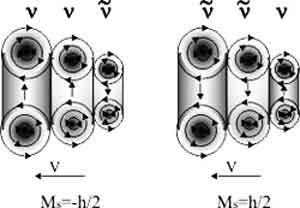 |
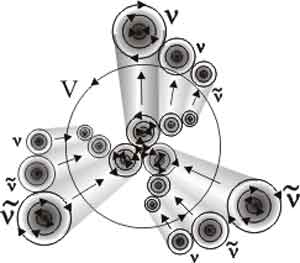
| Block diagram of muon neutrinos and muon antineutrinos. They are formed by three coaxial standing neutrino and antineutrino |
|
|
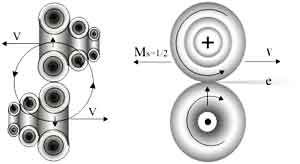 |
| The structure of the muon. It is like the structure of the electron |
|
|
 |
| Scheme c-quark - it is formed by joining the muon neutrino to muon |
|
|
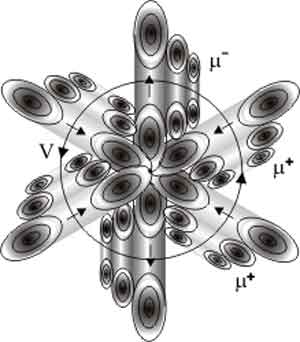 |
| Protons formed in the hot universe in binary collisions with quarks. After connecting to the quarks are regrouped into two muons + antimuonium or two pi-mesonÓ |
|
|
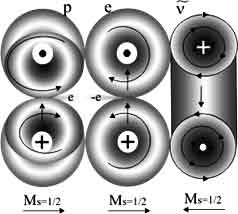 |
| A neutron is formed by joining the energetic proton and electron antineutrino |
Fully section in PDF format, view (Left Click) or download (Right Click) here. Leave your opinion in the guestbook.