How is this world?
 |
| Galileo Galilei |
 |
| Rene Descartes |
 |
| Isaac Newton |
 |
| Albert Einstein |
 |
| Michael Faraday |
 |
| James Clerk Maxwell |
 |
| Hermann Helmholtz |
 |
| Henry Lorenz |
 |
| Henri Poincare |
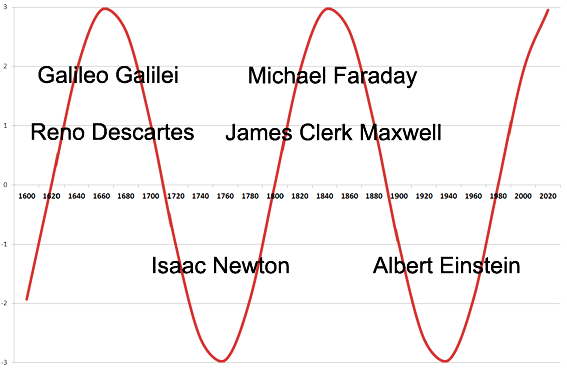
Fundamentals of modern ideas about the world created Galileo Galilei (1564-1642). He believed that the world is infinite, and that matter is eternal. All the processes occurring in nature, nothing is destroyed and is not generated - there is only a change in the relative position of the bodies or parts of them.
Since the time of Galileo's development of physics is in the form of the constant change of the absolute ages of rationalism and absolute formalism. The period up to 1740 was a period of a hundred years of complete domination Cartesians - supporters of the doctrine of Rene Descartes (1596-1650) of the vortex nature of matter. In particular, in 1690, Huygens published his treatise on the world, built on the hypothesis of the vortex air. Johann Bernoulli, his son Daniel Bernoulli, Maclaurin, Euler, Bio, Maupertuis, Leibniz, were supporters of the short-range air through the vortex. That Descartes and Huygens theoretically ground and gave clarity scientific discoveries of Galileo.
Next hundred years were marked by Newtonian physics (1643-1727). Greatest importance for the future was the work of M. Faraday (1791-1867). The son of a blacksmith, to learn to be a bookbinder, he became the founder of the theory of the electromagnetic field, discovered the laws of electromagnetic induction and the laws of electrolysis. He introduced the concept of lines of force, discovered the phenomenon of paramagnetism and diamagnetism, set the plane of polarization of light in a magnetic field. It was he who in 1832 suggested that the propagation of electromagnetic wave interactions is a process that takes place at a finite rate.
And then in the foreground figure of JC Maxwell (1831-1879). In 1861-62 years. appeared well-known model of the electromagnetic field of Maxwell. Current in it is seen as a progressive movement, but a manifestation of magnetism - the rotational movement of a mechanical ether. In 1871 there was the famous treatise "Electricity and Magnetism." Saw earlier in the rational interpretation of ethereal models of electromagnetic phenomena, Maxwell moved here to the relatively formal treatment issue. In his paper summarizes the two basic laws of electric and magnetic effects: Faraday's law of electromagnetic induction and Ampere's law for the magnetic forces caused by currents. Maxwell showed theoretically possible existence of electromagnetic waves and light pressure.
The figure shows a sine curve of change of periods of physical and rational-formal mathematical methods of describing the world in the last 400 years.
In purely formal channel developed and quantum mechanics, which was expelled from the air and over-Menen "virtual particles" that are in "probabilistic state." It was stated that the classical concepts are not valid in the quantum approach, the collapse of habitual foundations - a common phenomenon, and the objects present a microcosm clearly impossible. In short, quantum physics - is a world of illusion, which is available only to the initiated.
Of course, for this approach, there was good reason. After earlier attempts to simulate the electron as a solid indivisible ball of finite size, bearing surface evenly distributed electrical charge failed. Classical electron dimensions were determined from the condition of electromagnetic origin of its mass. To obtain experimental values ??of the intrinsic angular momentum of the electron-ball should rotate around its axis so fast that the line speed at the equator 170 times greater than the speed of light.
The models in the microcosm physics abandoned, much like foxes refusal of unripe grapes. By as much as a hundred years to the present day again prevailed phenomenological, abstract formal mathematical way of describing physical phenomena, when talking about the nature and mechanisms of the processes in the micro considered almost indecent.
Classical physics broke her teeth on the model of the electron. But the answers to questions about the nature of things not given, and quantum mechanics: it charge attached to the wave packet is still harder than the ball. Not rescued and mathematics - in the Schrodinger equation does not include a fundamental property of the electron, the spin, and the other wave characteristics, require special treatment. In fact, the phase velocity of the de Broglie wavelength than light and other characteristics - wavelength, frequency and phase - not related to the physical characteristics. Determine the amplitude of the wave function of the Schrodinger equation is not possible. It is found from the normalization conditions that the wave description is irrelevant.
Today, even the terminology is not completely clear: the matter - it is matter, and the field - is "special-by" kind of matter. So, the two faces of the matter? Especially because of the fundamental fields for more than thirteen. The same glitches in ether. Ether is not, and can not be, but there is a "physical vacuum", which has the following properties, and energy ether Maxwell could only envy, if it existed.
A self electromagnetic field, which, on one hand, is defined as related oscillations of electric and magnetic fields, and on the other hand, as a set of rays - photons. But the electric field is generated by the electric charge, the magnetic field is created by the motion of the charge. There is no charge photons, so no electric or magnetic fields - and then there is nothing to hesitate! Electromagnetic waves travel in a vacuum - what then there fluctuates? And somebody can explain the role of photons in the electromagnetic induction, an electromotive force on the secondary side of the transformer?
It is believed that the elementary particles and structureless point, however, these terms have mass, charge, spin and magnetic moment. Common sense tells us that "the electron is as inexhaustible as the atom." We speak of "strong", "weak", "electromagnetic" and "gravitational" interactions. We do not agree: but what is the nature of these phenomena? After separation of the types of interactions exist only in our heads. Forces that arise when these interactions are of the same nature? In general, in the microcosm and macrocosm are the same or different laws?
What questions answers vortex model microcosm?
In physics, there is a model in which would have been given a clear understanding of the nature of the microcosm. No answer the simplest questions about the basic physical concepts and phenomena:
- What is mass?
- What is gravity?
- What is the charge of the particle?
- What is the electric field?
- What is the magnetic field?
- What are electromagnetic waves?
- How is the interaction between charges?
- What is the structure of elementary particles and photons?
- Where to find antimatter?
- Where does the quantization in a microcosm?
- How the electrons of the atoms interact with photons?
- What is the strong interaction?
- How is an atom?
- What holds atoms in molecules?
- What is the "dark energy"?
- What does the "dark matter"?
- How did the universe?
 |
| Claudius Ptolemy |
 |
| Johannes Kepler |
 |
| Johann Bernoulli |
 |
| Josef Jon Thomson |
 |
| William Thomson, Lord Kelvin |
 |
| Max Planck |
 |
| Niels Bohr |
 |
| Werner Heisenberg |
Fully section in PDF format, view (Left Click) or download (Right Click) here. Leave your opinion in the guestbook.